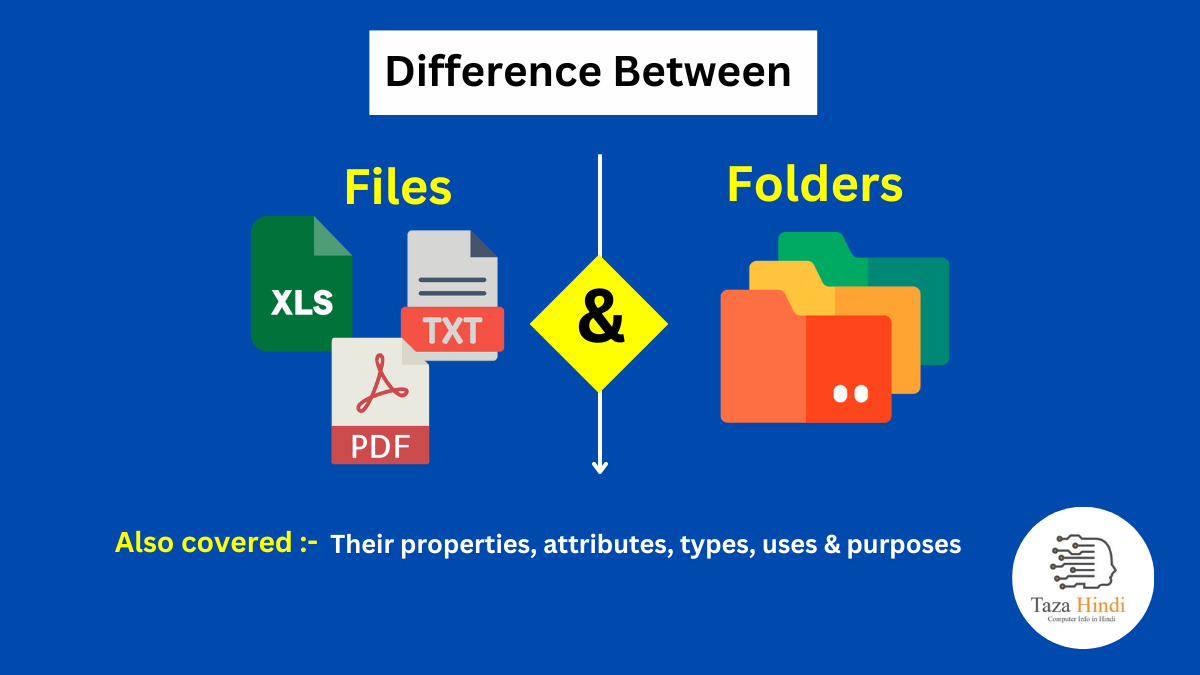
In the vast digital landscape, it is essential to have a structured system for managing and organizing information. Files and folders play a crucial role in this process, helping us keep our digital lives in order. In this article, you will get complete information about what is file and folder, their properties and attributes, their types, uses, purpose and what are the difference between file and folder.
What is a File?
A file can be thought of as a digital container that stores information. It can be a document, an image, a video, an audio recording, or any other form of data. Files are typically created and accessed using software applications specifically designed to handle their respective formats. They are identified by a unique name and extension, which indicates their file type.
File properties and attributes
Files possess various properties and attributes that provide valuable information about them. These include:
- File Name: The name assigned to a file, often chosen to reflect its content or purpose.
- File Extension: The three or four-letter code at the end of a file name, indicating its format and the software required to open it. For example, “.docx” for a Microsoft Word document or “.jpg” for an image file.
- File Size: The amount of space the file occupies on a storage device, typically measured in bytes, kilobytes, megabytes, or gigabytes.
- File Type: The category or format to which a file belongs, such as text, image, audio, video, or executable.
- Date Created/Modified: The date and time when the file was initially created or last modified.
Also Read : Difference between Static and Dynamic Memory Allocation
Types of Files and their uses
There are numerous file types, each serving a specific purpose and requiring a compatible software application for viewing, editing, or executing. Here are some common file types and their uses:
- Text Files: These files contain plain text or formatted text and are commonly used for storing documents, code, or configuration files.
- Image Files: Image files store visual content, such as photographs, illustrations, or graphics, in formats like JPEG, PNG, or GIF.
- Audio Files: Audio files capture sound and music, often stored in formats like MP3, WAV, or AAC.
- Video Files: Video files contain moving images and are typically stored in formats like MP4, AVI, or MOV.
- Executable Files: These files contain instructions that the computer’s operating system can execute. They allow software applications or programs to run on the system.
Also Read : Difference between Compiler and Assembler
What is a Folder?
A folder is a digital organizational container used to group and store related files. Also known as directories, folders provide a hierarchical structure for organizing files and subfolders. They help to create a logical system for managing data, making it easier to locate and access specific files.
Characteristics of Folder
Folders possess several characteristics that contribute to effective data organization:
- Hierarchy: Folders can be organized in a hierarchical manner, allowing for nesting of subfolders within parent folders. This hierarchical structure facilitates logical categorization and enables a systematic organization of files.
- Name and Label: Like files, folders have names to identify and differentiate them from one another. Descriptive folder names provide meaningful context and make it easier to navigate through the file system.
- Contents: Folders can contain both files and subfolders, creating a structured environment for organizing related data. This allows for the grouping of similar files together, enhancing efficiency and accessibility.
Also Read : Difference between Algorithm and Program
Purpose of Folders in organizing files
Folders serve various purposes in organizing files:
- Categorization: Folders enable the categorization of files based on specific criteria, such as project type, date, topic, or department. This categorization simplifies file management and retrieval, saving time and reducing clutter.
- Accessibility: Folders provide a centralized location for storing related files, making it easier to locate and access them quickly. This improves workflow efficiency and enhances collaboration among team members.
- Organization: By grouping files into folders, it becomes easier to maintain a structured file system. This organization helps prevent data fragmentation and promotes a streamlined approach to file management.
Also Read : Difference between Variable and Constant
Uses of Folders
Folders find applications in various areas, including:
- Personal File Management: Folders help individuals organize personal files, such as documents, photos, music, and videos, into meaningful categories. This enables efficient retrieval and minimizes the risk of data loss.
- Business File Organization: In a business environment, folders are instrumental in managing and organizing files related to projects, clients, departments, or processes. This promotes efficient collaboration, knowledge sharing, and document version control.
- Web Development: Folders play a crucial role in web development by organizing website files, such as HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and media assets. A well-structured folder system simplifies website maintenance, updates, and deployment.
Functionality of Folders
Folders provide several functionalities that aid in file management:
- Creation and Deletion: Folders can be created or deleted as needed, allowing for the dynamic organization of files. This flexibility enables the adaptation of the file system to changing requirements.
- Moving and Copying: Files and folders can be moved or copied between different folders, facilitating reorganization or duplication of data. This flexibility allows for efficient file management and backup strategies.
- Searching and Filtering: Modern operating systems and file management software provide search and filtering capabilities, making it easier to locate files within folders based on various criteria, such as name, date, or file type.
Also Read : What is Moonlighting, Pros and Cons of Moonlighting
Difference between File and Folder
| File | Folder |
| A file is a container that stores information or data, such as a document, image, or video. It represents a single unit of data with its own content and properties. | A folder is a container used to organize and categorize files. It acts as a directory or a storage location for grouping related files and subfolders. |
| Files are self-contained entities with their own content, properties, and file extensions that determine their format and the software required to open them. They are typically identified by unique names and extensions. | Folders do not contain content directly but instead serve as organizational structures. They can contain multiple files and subfolders, allowing for a hierarchical arrangement of data. |
| Files are accessed directly by opening them with the appropriate software applications. They can be stored in any location on a storage device, such as the root directory or within a folder. | Folders, on the other hand, are used to group and organize files, making them easier to locate and access. By navigating through the folder hierarchy, users can quickly find the desired files. |
| Files do not have a hierarchical structure by themselves. They exist independently and can be located in different locations within a file system. | Folders provide a hierarchical structure for organizing files. They can be nested within each other, creating a parent-child relationship. This hierarchy allows for logical categorization and facilitates systematic organization of data. |
| Files are typically managed individually, and their organization relies on the user’s ability to name and store them in appropriate locations. | Folders provide a systematic approach to file organization. They allow for the categorization and grouping of files based on specific criteria, such as project type, date, or topic. Folders simplify file management, improve workflow efficiency, and make it easier to maintain a structured file system. |
Conclusion
Files and folders are indispensable components of organizing and managing our digital lives. Understanding their differences, properties, and functionalities is crucial for maintaining an efficient file system. By leveraging the power of folders and using them effectively to categorize and store files, individuals and businesses can streamline their workflows, improve collaboration, and enhance overall productivity.
FAQs
-
Can a file exist without being in a folder?
Yes, files can exist without being in a folder. They can be stored in the root directory or any other location on a storage device.
-
Can a folder contain other folders?
Yes, folders can contain other folders, creating a hierarchical structure. This nesting of folders allows for a more granular organization of files.
-
Can I change the name of a file or folder?
Yes, you can change the name of a file or folder at any time. Renaming provides flexibility in managing and organizing your data.
-
Can files and folders be encrypted for security?
Yes, modern operating systems and file management software often provide encryption features to protect sensitive files and folders from unauthorized access.
-
Are there any limits to the number of files or folders that can be created?
The limits on the number of files or folders depend on the operating system and file system used. Different systems have different constraints, but for most practical purposes, the limits are large enough to accommodate a vast number of files and folders.