In the realm of modern communication, the term “Transmission Impairment” might sound technical, but its significance in ensuring the seamless flow of data and information cannot be overstated. From the way your smartphone connects to the internet to how television signals are delivered to your screen, understanding transmission impairment is essential.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of transmission impairment, exploring what is transmission impairment, its importance, causes, types, measurement and analysis, and what ate the techniques used to mitigate its effects.
What is Transmission Impairment?
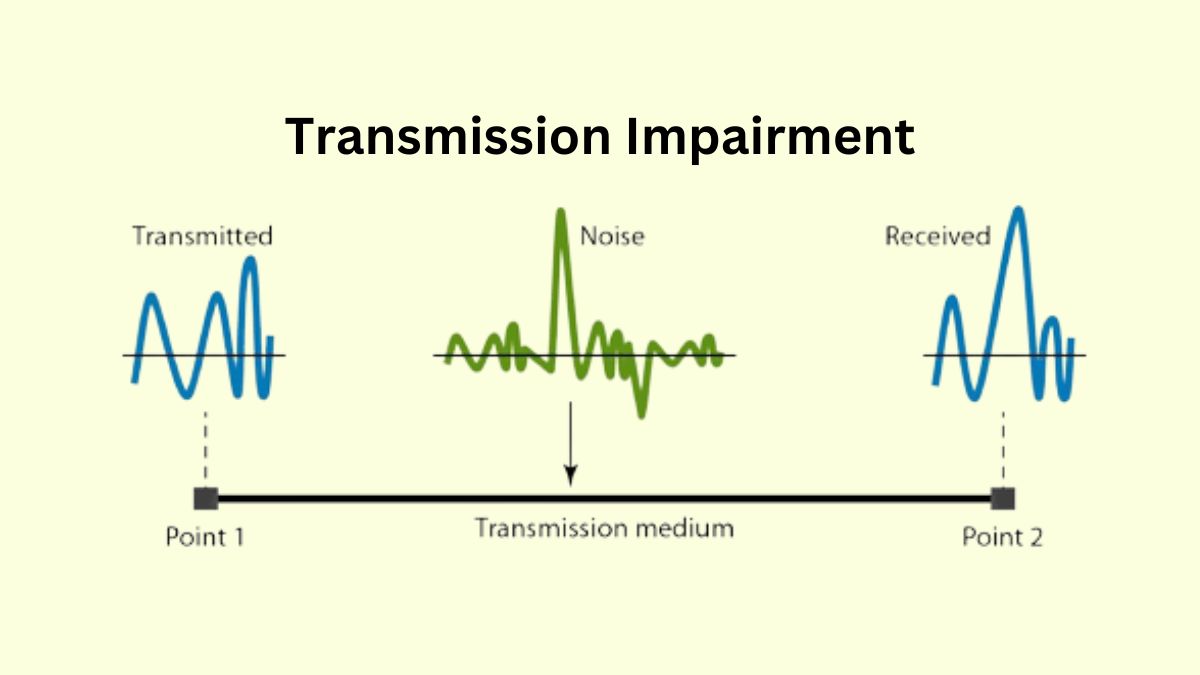
Transmission impairment is a phenomenon that affects the quality and integrity of signals during data transmission. Whether it’s your voice during a phone call or the digital information sent over the internet, transmission impairment can disrupt the signal, leading to data errors, drops in quality, or even complete loss of communication. To appreciate its importance fully, let’s explore its significance.
What is the importance of Transmission Impairment?
Understanding the importance of transmission impairment is crucial because it affects the reliability and effectiveness of communication systems across various domains, including telecommunications, data networks, broadcasting, and more. Transmission impairment can result in:
- Degraded signal quality: This can manifest as noise, distortion, or interference, affecting the clarity and integrity of the data being transmitted.
- Reduced data rates: Impairments can lead to a lower effective data transmission rate, impacting the efficiency of communication systems.
- Increased error rates: Transmission impairment can introduce errors in the received data, necessitating error correction mechanisms.
- Dropped connections: In severe cases, it can cause complete loss of communication, which can be especially critical in applications like emergency services and critical infrastructure.
What are the causes of Transmission Impairment?
Transmission impairment can arise from various factors, and it’s essential to recognize the primary causes:
1. Attenuation:
- Explanation: Attenuation refers to the reduction in signal strength as it travels through a medium. It is primarily caused by the natural resistance and energy loss in transmission lines.
- Effects: Attenuation leads to a decrease in signal strength, which can result in weaker, noisier signals and ultimately limit the transmission distance.
2. Noise:
- Explanation: Noise includes any unwanted random signals that get added to the intended signal during transmission. Sources of noise can include electromagnetic interference, thermal noise, and crosstalk.
- Effects: Noise degrades the quality of the signal, making it harder to distinguish the original data, leading to higher error rates.
3. Interference:
- Explanation: Interference occurs when external signals disrupt the intended communication, often due to overlapping frequencies or improper shielding.
- Effects: Interference can distort the signal, causing data corruption or complete signal disruption.
Types of Transmission Impairments
To comprehend transmission impairment fully, it’s essential to categorize it into different types:
1. Attenuation:
- Explanation and Causes: Attenuation occurs due to the natural resistance and energy loss in transmission lines, including electrical resistance and dielectric loss.
- Effects on Signal Quality: Attenuation weakens the signal, leading to signal loss, degradation, and reduced transmission distances.
2. Noise:
- Explanation and Types: Noise encompasses various unwanted signals like thermal noise, electromagnetic interference (EMI), and crosstalk.
- Sources of Noise: Noise can originate from external sources, internal electronic components, and environmental factors.
- How Noise Affects Data Transmission: Noise interferes with the signal, making it challenging to receive the data accurately, increasing error rates.
3. Interference:
- Types of Interference: Interference can be classified as electromagnetic interference (EMI), radio frequency interference (RFI), and even self-interference.
- Common Sources of Interference: Sources include nearby electronic devices, radio transmissions, and even signal reflections.
- Consequences of Interference: Interference disrupts the signal, potentially leading to data corruption and signal loss.
How to measuring and analyzing Transmission Impairment?
Measuring and analyzing transmission impairment is essential for maintaining reliable communication systems. Common techniques and metrics include:
- Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR): SNR measures the strength of the desired signal relative to background noise. Higher SNR values indicate better signal quality.
- Bit Error Rate (BER): BER measures the number of erroneous bits in a data transmission, providing insight into the integrity of the communication link.
- Eye Diagrams: Eye diagrams are graphical representations of signal quality and can reveal distortions and noise in the transmitted data.
- Importance of Proper Measurement and Analysis: Accurate measurement and analysis of transmission impairment are critical for diagnosing and addressing issues in communication systems, ensuring data integrity, and improving system performance.
Techniques for Mitigating Transmission Impairment
Mitigating transmission impairment is essential for maintaining reliable communication. Various techniques are employed to minimize its impact:
- Equalization: Equalization techniques help compensate for signal distortions, especially in long-distance communication, to improve signal quality.
- Error Correction Codes: Error correction codes add redundancy to data, enabling receivers to correct errors caused by noise and interference.
- Noise Reduction Strategies: Strategies like shielding, filtering, and proper grounding can reduce noise and interference.
- Frequency Bands and Modulation Techniques: Using specific frequency bands and modulation schemes can enhance the ability to transmit data reliably in different environments.
Video Tutorial on What is Transmission Impairment
Conclusion
Transmission impairment may be a technical concept, but its implications are felt throughout our modern world of communication. From the quality of our phone calls to the clarity of our television broadcasts, understanding and addressing transmission impairment is crucial. By recognizing its causes, types, and measurement techniques, and by employing mitigation strategies, we can ensure that our communication systems operate with the utmost reliability and efficiency. Transmission impairment may be a challenge, but with the right knowledge and tools, it becomes a hurdle we can easily overcome in our interconnected world.
Also Read :